Connecting ClickHouse to external data sources with JDBC
Using JDBC requires the ClickHouse JDBC bridge, so you will need to use clickhouse-local on a local machine to stream the data from your database to ClickHouse Cloud. Visit the Using clickhouse-local page in the Migrate section of the docs for details.
Overview: The ClickHouse JDBC Bridge in combination with the jdbc table function or the JDBC table engine allows ClickHouse to access data from any external data source for which a JDBC driver is available:
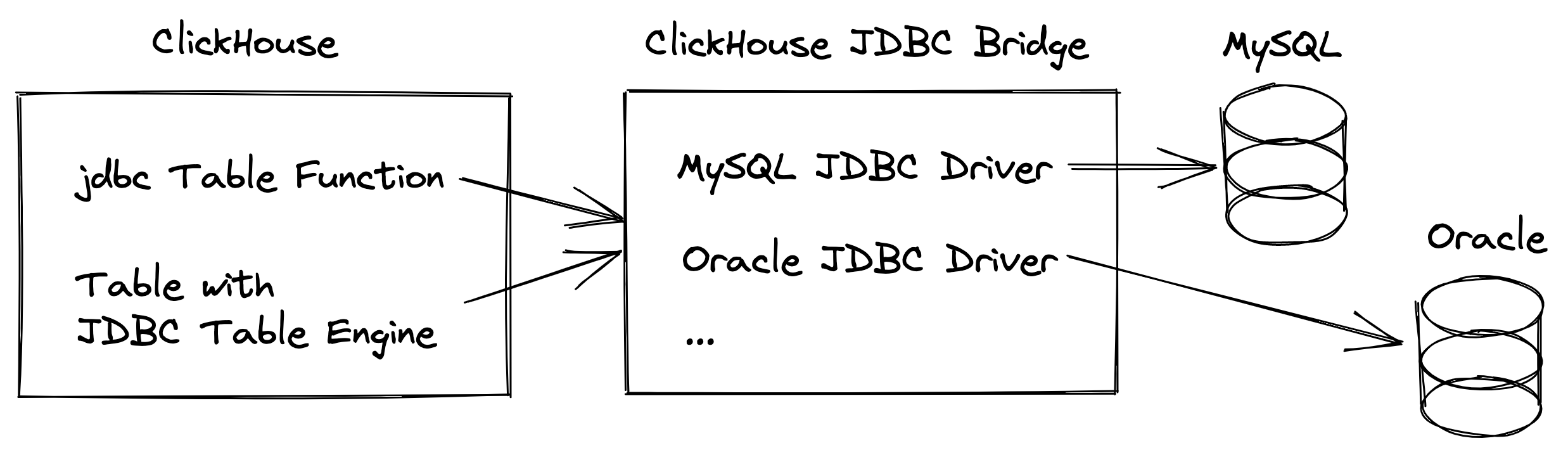
This is handy when there is no native built-in integration engine, table function, or external dictionary for the external data source available, but a JDBC driver for the data source exists.
You can use the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge for both reads and writes. And in parallel for multiple external data sources, e.g. you can run distributed queries on ClickHouse across multiple external and internal data sources in real time.
In this lesson we will show you how easy it is to install, configure, and run the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge in order to connect ClickHouse with an external data source. We will use MySQL as the external data source for this lesson.
Let's get started!
Install the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge locally
The easiest way to use the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge is to install and run it on the same host where also ClickHouse is running:
Let's start by connecting to the Unix shell on the machine where ClickHouse is running and create a local folder where we will later install the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge into (feel free to name the folder anything you like and put it anywhere you like):
mkdir ~/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge
Now we download the current version of the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge into that folder:
cd ~/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge
wget https://github.com/ClickHouse/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge/releases/download/v2.0.7/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge-2.0.7-shaded.jar
In order to be able to connect to MySQL we are creating a named data source:
cd ~/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge
mkdir -p config/datasources
touch config/datasources/mysql8.json
You can now copy and paste the following configuration into the file ~/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge/config/datasources/mysql8.json:
{
"mysql8": {
"driverUrls": [
"https://repo1.maven.org/maven2/mysql/mysql-connector-java/8.0.28/mysql-connector-java-8.0.28.jar"
],
"jdbcUrl": "jdbc:mysql://<host>:<port>",
"username": "<username>",
"password": "<password>"
}
}
in the config file above
- you are free to use any name you like for the datasource, we used
mysql8 - in the value for the
jdbcUrlyou need to replace<host>, and<port>with appropriate values according to your running MySQL instance, e.g."jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306" - you need to replace
<username>and<password>with your MySQL credentials, if you don't use a password, you can delete the"password": "<password>"line in the config file above - in the value for
driverUrlswe just specified a URL from which the current version of the MySQL JDBC driver can be downloaded. That's all we have to do, and the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge will automatically download that JDBC driver (into a OS specific directory).
Now we are ready to start the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge:
cd ~/clickhouse-jdbc-bridge
java -jar clickhouse-jdbc-bridge-2.0.7-shaded.jar
We started the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge in foreground mode. In order to stop the Bridge you can bring the Unix shell window from above in foreground and press CTRL+C.
Use the JDBC connection from within ClickHouse
ClickHouse can now access MySQL data by either using the jdbc table function or the JDBC table engine.
The easiest way to execute the following examples is to copy and paste them into the clickhouse-client or into the Play UI.
- jdbc Table Function:
SELECT * FROM jdbc('mysql8', 'mydatabase', 'mytable');
As the first paramter for the jdbc table funtion we are using the name of the named data source that we configured above.
- JDBC Table Engine:
CREATE TABLE mytable (
<column> <column_type>,
...
)
ENGINE = JDBC('mysql8', 'mydatabase', 'mytable');
SELECT * FROM mytable;
As the first paramter for the jdbc engine clause we are using the name of the named data source that we configured above
The schema of the ClickHouse JDBC engine table and schema of the connected MySQL table must be aligned, e.g. the column names and order must be the same, and the column data types must be compatible
Install the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge externally
For a distributed ClickHouse cluster (a cluster with more than one ClickHouse host) it makes sense to install and run the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge externally on its own host:
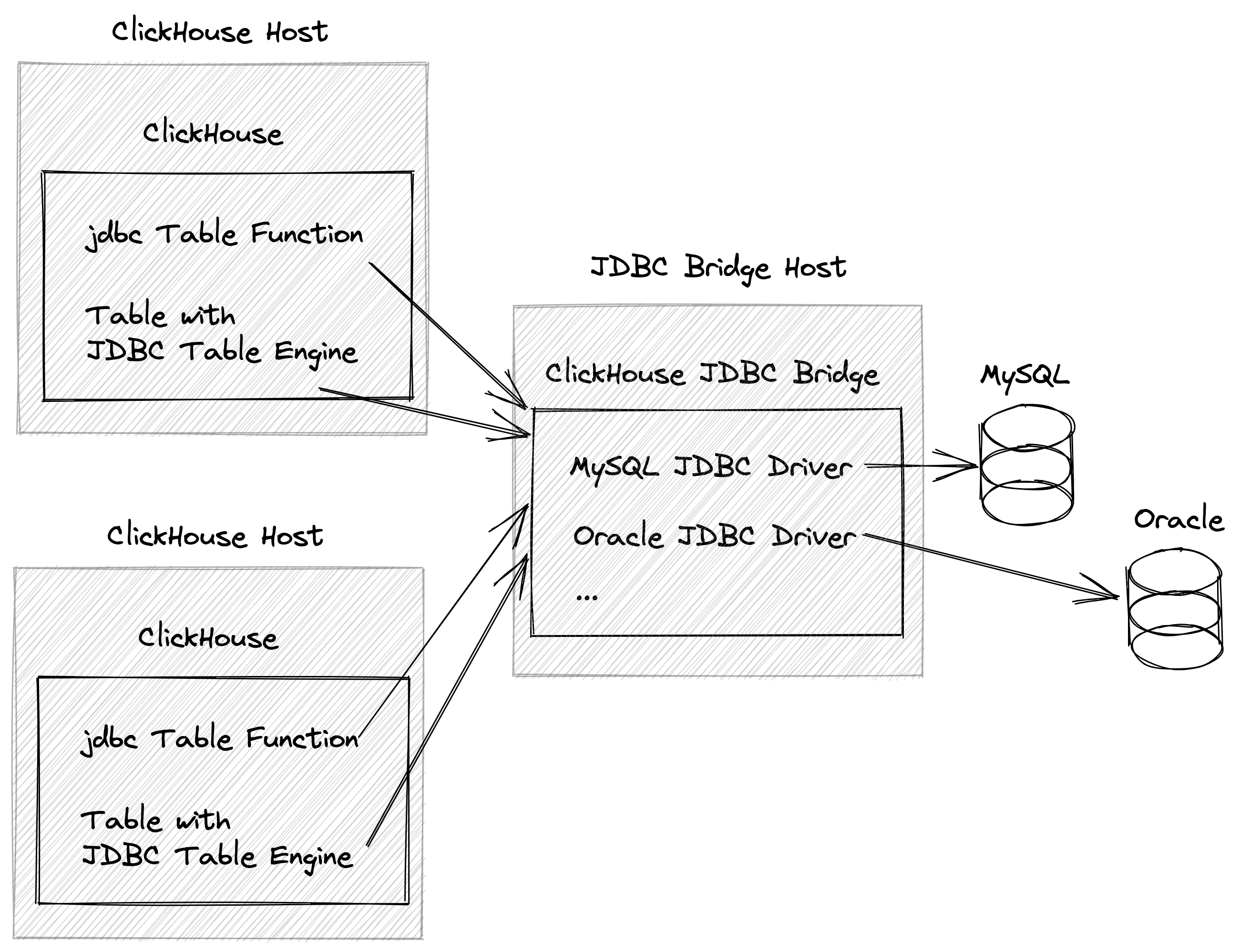
This has the advantage that each ClickHouse host can access the JDBC Bridge. Otherwise the JDBC Bridge would need to be installed locally for each ClickHouse instance that is supposed to access external data sources via the Bridge.
In order to install the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge externally, we do the following steps:
-
We install, configure and run the ClickHouse JDBC Bridge on a dedicated host by following the steps described in section 1 of this guide.
-
On each ClickHouse Host we add the following configuration block to the ClickHouse server configuration (depending on your chosen configuration format, use either the XML or YAML version):
- XML
- YAML
<jdbc_bridge>
<host>JDBC-Bridge-Host</host>
<port>9019</port>
</jdbc_bridge>
jdbc_bridge:
host: JDBC-Bridge-Host
port: 9019
- you need to replace
JDBC-Bridge-Hostwith the hostname or ip address of the dedicated ClickHouse JDBC Bridge host - we specified the default ClickHouse JDBC Bridge port
9019, if you are using a different port for the JDBC Bridge then you must adapt the configuration above accordingly

